Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in different high-risk facility types during a period of Delta variant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Min Jei Lee, Myung-Jae Hwang, Dong Seob Kim, Seon Kyeong Park, Jihyun Choi, Ji Joo Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Young-Man Kim, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):418-426. Published online October 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0188
- 1,308 View
- 44 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 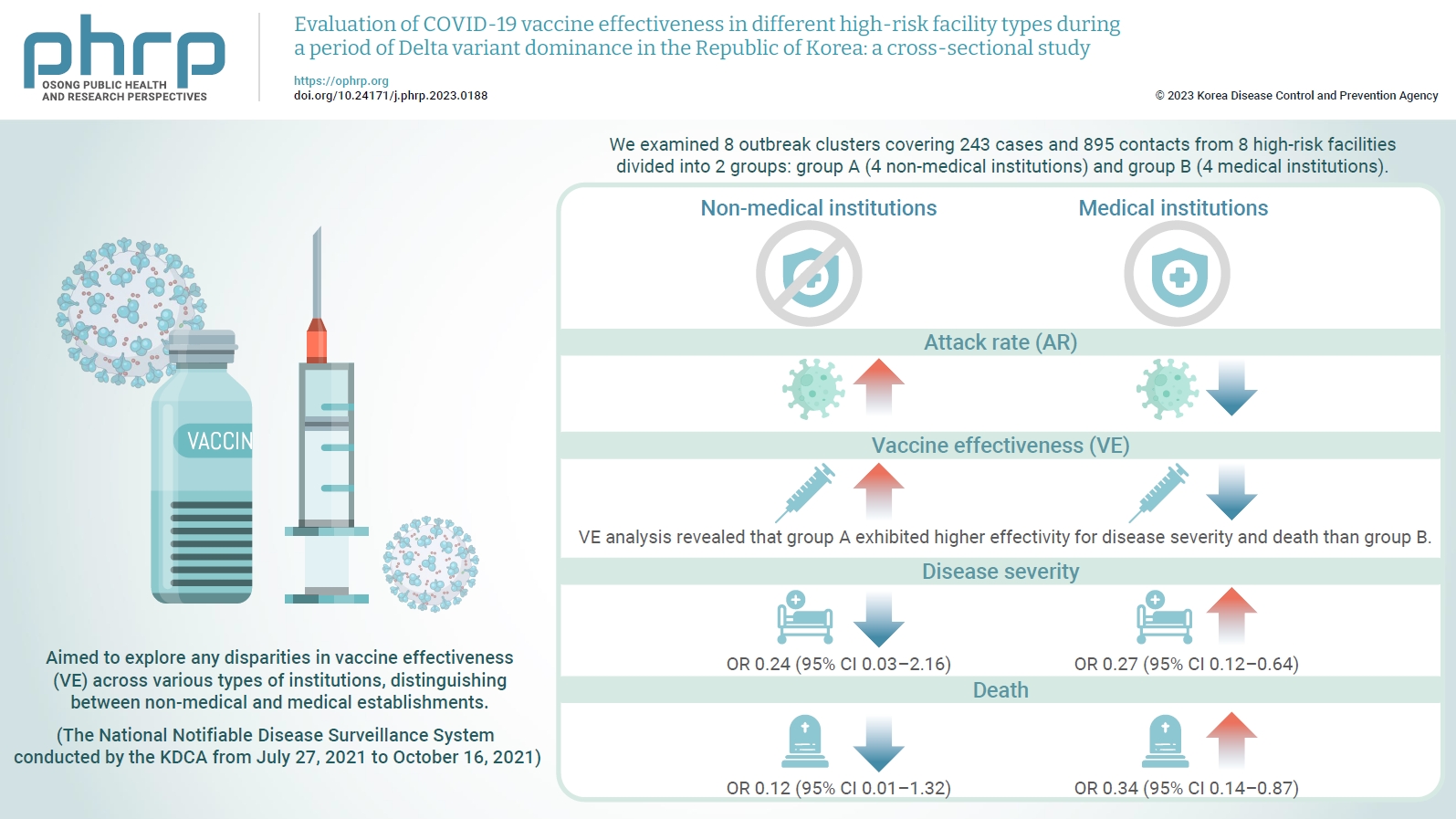
- Objectives
We evaluated the effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in high-risk facilities in the Republic of Korea during the period when the highly transmissible Delta variant was prevalent. Additionally, we aimed to explore any disparities in vaccine effectiveness (VE) across various types of institutions, specifically distinguishing between non-medical and medical establishments. Methods: We examined 8 outbreak clusters covering 243 cases and 895 contacts from 8 high-risk facilities divided into 2 groups: group A (4 non-medical institutions) and group B (4 medical institutions). These clusters were observed from July 27, 2021 to October 16, 2021 for the attack rate (AR) and VE with respect to disease severity. A generalized linear model with a binomial distribution was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) for disease severity and death. Results: AR was notably lower in group B (medical institutions). Furthermore, VE analysis revealed that group A exhibited higher effectivity for disease severity and death than group B. The OR for disease severity was 0.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–2.16) for group A and 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.64) for group B, with the OR for death at 0.12 (95% CI, 0.01–1.32) in group A and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.14–0.87) in group B. Conclusion: Although VE may vary across institutions, our findings underscore the importance of implementing vaccinations in high-risk facilities. Customized vaccination programs, tailored response plans, and competent management personnel are essential for effectively addressing and mitigating public health challenges.
Brief Report
- Early countermeasures to COVID-19 at long-term care facilities in Gwangju Metropolitan City, Republic of Korea
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jieun Kim, Yoon Suk Jang, Hanul Park, Jong Mu Kim, Young Joon Park, So-Yeon Ryu, Jun Hwi Cho, So Yeong Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):59-65. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0293
- 1,937 View
- 79 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 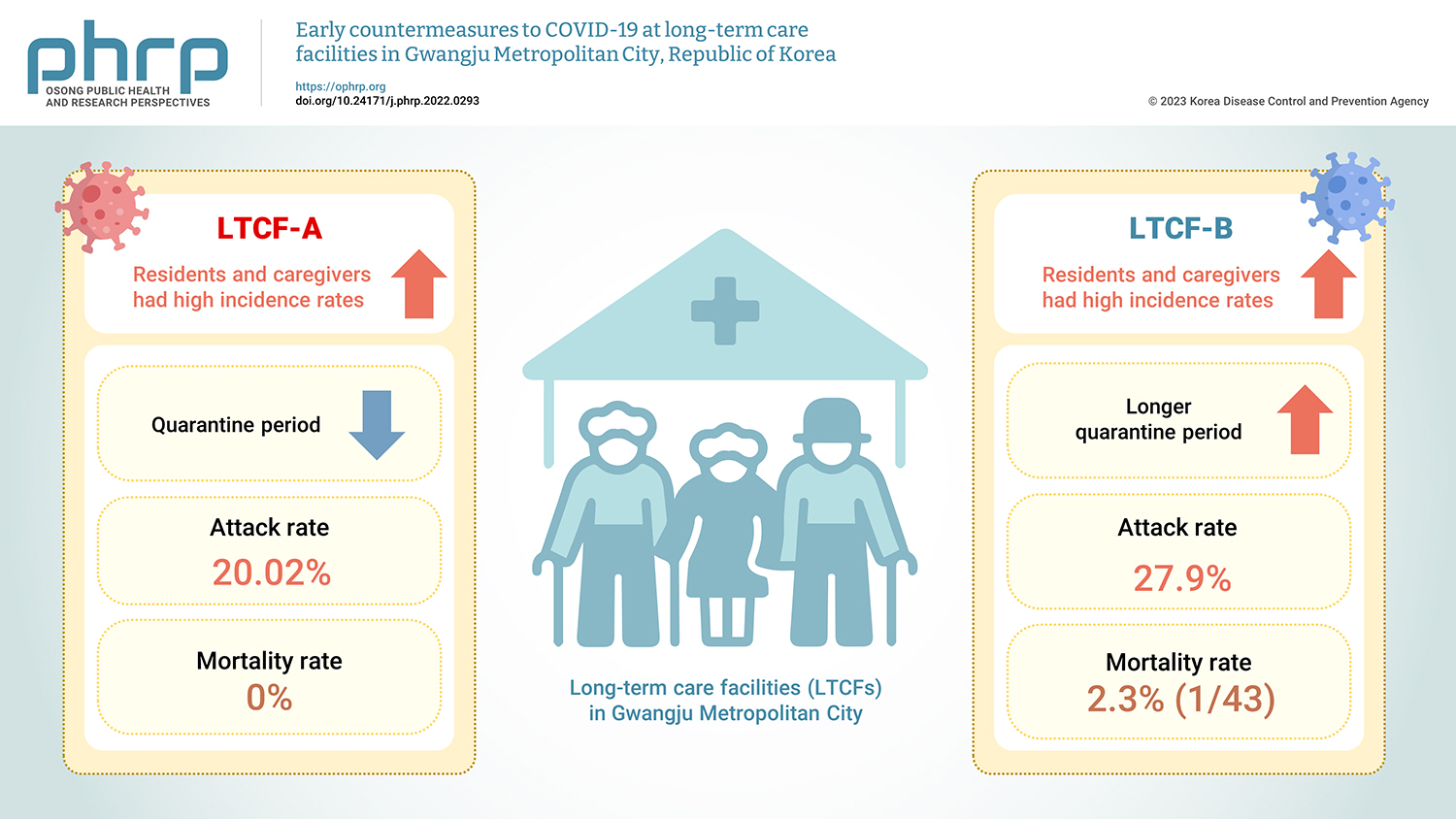
- Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has continued since its first detection in the Republic of Korea on January 20, 2020. This study describes the early countermeasures used to minimize the risk of COVID-19 outbreaks during cohort quarantine and compares the epidemiological characteristics of 2 outbreaks in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) in Gwangju Metropolitan City in summer 2020. Methods: An epidemiological investigation was conducted via direct visits. We investigated epidemiological characteristics, including incidence, morbidity, and mortality rates, for all residents and staff members. Demographic characteristics were analyzed using a statistical program. Additionally, the method of managing infection in LTCFs is described. Results: Residents and caregivers had high incidence rates in LTCF-A and LTCF-B, respectively. LTCF-B had a longer quarantine period than LTCF-A. The attack rate was 20.02% in LTCF-A and 27.9% in LTCF-B. The mortality rate was 2.3% (1/43) in LTCF-B, the only facility in which a COVID-19 death occurred. Conclusion: Extensive management requires contact minimization, which involves testing all contacts to mitigate further transmission in the early stages of LTCF outbreaks. The findings of this study can help inform and prepare public health authorities for COVID-19 outbreaks, particularly for early control in vulnerable facilities.


 First
First Prev
Prev


